Segment routing has been well received because it simplifies the network and allows it to scale a lot more efficiently than MPLS networks by reducing the number of protocols required. Segment routing also makes IPv6 more relevant and it is the next step in making networks as scalable as possible.
Scalability of the network is essential because the number of network devices and the amount of traffic are increasing rapidly over time. Cisco has forecasted that the amount of traffic will triple between 2013 and 2018. This means that the network must adapt extremely quickly. (Nokia Oyj 2016a.) Segment routing is also the answer to the needs of software defined networking. Certain applications require the lowest latency path but a traditional routing protocol may forward the traffic through a higher latency higher bandwidth route. Source routing enables the application to choose the lower latency path if necessary.
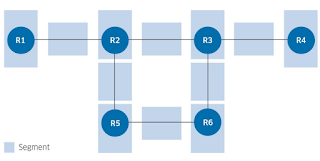
Figure above shows which parts of the network receive their own segment identifier. Segment identifiers are encoded as either MPLS labels or IPv6 addresses. Each node and link get their own segment identifier in a segment routing network. These segment identifiers are globally significant in the segment routing domain, which makes troubleshooting the network easier than in MPLS LDP networks where labels have only local significance.
Segment routing does not require LDP or RSVP-TE to work. The label distribution is handled by IGP. RSVP-TEs downside is that it must maintain a state on each router along the path, which makes it scale poorly. The only state that segment routing traffic engineering (SR-TE) must maintain is at the ingress router. This allows the network to scale significantly better than with the older technologies.
The introduction of segment routing has also renewed the interest in stateful active path computation element (PCE). PCE is a traffic engineering controller that manages the network by allocating the correct paths and resources to the services that need them. The use of PCE also makes software defined networking (SDN) more appealing in WAN networks. The simplification of the network allows features like bandwidth calendaring and bandwidth on demand which are needed by the SDN applications.
SEGMENT IDENTIFIER
Segment identifiers (SIDs) are used in the SR network to identify different parts of the network. Segment routing reduces the number of labels required in the network because a label can indicate a whole path instead of just one hop to the next node like in RSVP-TE. Commonly used segment identifiers include Prefix, Adjacency and Anycast-SID.PREFIX-SID
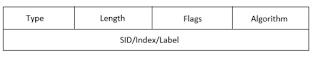
A prefix-SID is the SID of an IGP-prefix segment. A prefix-SID is a unique identifier within the SR/IGP domain. An IGP-prefix segment consists of the following fields: type, length, flags, algorithm and SID/Index/Label as shown in figure belowThe type field signifies the type of the packet. In this case, the type value is set to 3. Length is a variable that can be different for every label.
The flag field specifies how the prefix-SID should be handled. There are six different flags in total. Each flag can have a value of either 0 or 1. The behaviour of the packet changes depending on the flag values.
R-flag means that the prefix-SID is redistributed or from another level, for example a level-1 prefix-SID propagated to level-2. Redistribution means the flag has been redistributed by another protocol. N-flag specifies that the prefix-SID is a Node-SID which means that it refers to a router’s loopback address. N flag can be unset to prevent it from referring to a router. This is needed when configuring an anycast-SID.
P-flag prevents the PHP-operation from being applied to the prefix-SID when set. P-flag can be disabled to enable the PHP-operation. PHP reduces the load on edge routers. E-flag specifies that the upstream routers must have an explicit-null value for that prefix-SID. A label with explicit-null value will be popped when received by an LSR.
V-flag is unset by default, which means that the packet carries an index. If V flag is set, then the packet carries a local label value instead. An index value is used to determine the SID or label value. L-flag is also unset by default. If L flag is set, the prefix-SID is only locally significant. Locally significant labels are not distributed to other routers.
The algorithm field defines how the packet must be forwarded to its destination. A value 0 in the algorithm field signifies that the packet must take the Shortest Path First (SPF) computed by IS-IS. However, this SPF calculation can be overwritten by any router on the path that has a local policy. A value of 1 means that the Shortest Path First calculation is strict and cannot be overwritten by local policies.
The SID/Index/Label field contains an index that defines the offset in the label space. This can be used to calculate the SID of the segment.
Segment routing Node-SID or IGP Node Segment identifies a specific router in the network by using the nodes loopback address as the prefix. Node-SID can be used to navigate from any point of the segment routing network to a segment routing node (LSR) with a corresponding Node-SID.
ADJACENCY-SID
An adjacency segment identifier (Adj-SID) is used by a segment routing node to advertise its links to adjacent routers. Adj-SIDs are not unique within the SR domain by default. Adj-SIDs are allocated from the dynamic label range which starts from 24000 in IOS-XRv. Multiple links can have the same Adj-SID.Adjacency-SID consists of Type, Length, Flags, Weight and SID/Index/Label fields. Adj-SIDs suggested type value is 31. Length is variable on label-to-label basis.
The flag field has the following flag settings: F, B, V, L and S. F-flag is the address-family flag. If the F-flag is set, the adjacency is IPv6. If left unset, the adjacency is IPv4. B-flag is the Backup-flag. If backup-flag is set, the adjacencySID can be protected by TI-LFA. More information about TI-LFA can be found in Chapter 4.6.
V-flag signifies that the Adj-SID has a value. It is set by default. L-flag is the Local-flag. It is set by default and means that the Adj-SID is locally significant. S-flag indicates that the Adj-SID is used for multiple adjacencies when set.
The weight field determines the Adj-SIDs weight in load-balancing scenarios where there are multiple paths with the same Adj-SID. For example, link A and link B both have Adj-SID of 24005. Link A has a weight of 1 and link B has a weight of 2. The traffic will be load-balanced between link A and B in 1:2 ratio.
The SID/Index/Label field contains either a local label, an index defining the offset in Label space or an IPv6 address. The local label requires that V and L flags are set. However, if they are unset, the field will be an index field. An IPv6 address requires that V-flag is set. L-flag can be either set or unset depending whether the IPv6 address is globally or locally significant.